
It’s well-known that about half of all proteins typically expressed in a cell undergo a major type of post-translational modification (PTM) — glycosylation — which adds covalently linked sugars to polypeptide chains. This PTM can significantly impact processes like cell adhesion, molecular trafficking, clearance, and signal transduction.
So understanding the effects of glycosylation or deglycosylation (removal of carbohydrates from glycoproteins) on your protein are really important. If you’re developing a therapeutic protein, for example, you might want to know if glycosylation has any negative effects on its bioactivity, safety, stability, etc.
From a practical perspective, deglycosylation can not only help with identifying sites of glycosylation, but it can also help with simplifying proteins for easier analysis (e.g. mass spec) or removal of sample heterogeneity for X-ray crystallography.
What are some of the common ways to deglycosylate your protein?
In eukaryotes, the most common glycosylation modifications in the secretory pathway are additions at consensus asparagine residues (N-linked); or at serine or threonine residues (O-linked). It’s helpful to use glycosidases — enzymes that break bonds between mono- or oligosaccharides and other compounds — that hydrolyze N-glycosyl compounds and O-glycosyl compounds. PNGaseF is commonly used for the removal of N-linked glycans. For O-glycans, OglyZORR from Genovis can be used to remove the O-linked carbohydrates. OglyZOR specifically hydrolyzes core 1 type O-glycans on native glycoproteins. Combining OglyZOR and PNGaseF facilitates the evaluation of complex biopharmaceuticals like Etanercept, shown below (figure courtesy of Genovis). Etanercept is a fusion protein for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
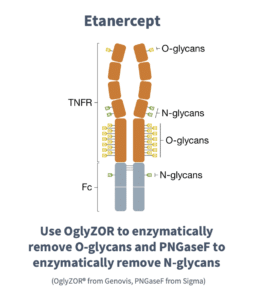
What effect does deglycosylation have on your protein?
Amongst other things, deglycosylation can affect the thermal stability and aggregation of your protein. And, instrumentation such as Prometheus can help to examine these attributes when you deglycosylate the various sites on your protein.
Removing just the N-glycans destabilizes Etanercept but doesn’t cause aggregation. Secondly, Etanercept is slightly stabilized when removing just the O-glycans and aggregation is only seen above 80 °C. Finally, the highest amount of destabilization and aggregation is seen when removing both O- and N-glycans.
Enzymes and samples kindly provided by ![]()

Whether you’re looking to examine the effects of glycosylation or deglycosylation on the stability or aggregation of your protein, Prometheus can help.





















